
A turbine is a rotary engine that extracts energy from a fluid flow. Claude Burdin coined the term from the Latin turbinis, or vortex during an 1828 engineering competition. The simplest turbines have one moving part, a rotor assembly, which is a shaft with blades attached. Moving fluid acts on the blades, or the blades react to the flow, so that they rotate and impart energy to the rotor. Early turbine examples are windmills and water wheels.
Gas, steam, and water turbines usually have a casing around the blades that focuses and controls the fluid. The casing and blades may have variable geometry that allows efficient operation for a range of fluid-flow conditions.
A device similar to a turbine but operating in reverse is a compressor or pump. The axial compressor in many gas turbine engines is a common example.
[edit] Theory of operation
A working fluid contains potential energy (pressure head) and kinetic energy (velocity head). The fluid may be compressible or incompressible. Several physical principles are employed by turbines to collect this energy:
- Impulse turbines
- These turbines change the direction of flow of a high velocity fluid jet. The resulting impulse spins the turbine and leaves the fluid flow with diminished kinetic energy. There is no pressure change of the fluid in the turbine rotor blades. Before reaching the turbine the fluid's pressure head is changed to velocity head by accelerating the fluid with a nozzle. Pelton wheels and de Laval turbines use this process exclusively. Impulse turbines do not require a pressure casement around the runner since the fluid jet is prepared by a nozzle prior to reaching turbine. Newton's second law describes the transfer of energy for impulse turbines.
- Reaction turbines
- These turbines develop torque by reacting to the fluid's pressure or weight. The pressure of the fluid changes as it passes through the turbine rotor blades. A pressure casement is needed to contain the working fluid as it acts on the turbine stage(s) or the turbine must be fully immersed in the fluid flow (wind turbines). The casing contains and directs the working fluid and, for water turbines, maintains the suction imparted by the draft tube. Francis turbines and most steam turbines use this concept. For compressible working fluids, multiple turbine stages may be used to harness the expanding gas efficiently. Newton's third law describes the transfer of energy for reaction turbines.
Turbine designs will use both these concepts to varying degrees whenever possible. Wind turbines use an airfoil to generate lift from the moving fluid and impart it to the rotor (this is a form of reaction). Wind turbines also gain some energy from the impulse of the wind, by deflecting it at an angle. Crossflow turbines are designed as an impulse machine, with a nozzle, but in low head applications maintain some efficiency through reaction, like a traditional water wheel. Turbines with multiple stages may utilize either reaction or impulse blading at high pressure. Steam Turbines are usually more impulse while Gas Turbines more reaction type designs. At low pressure the operating fluid medium expands in volume for small changes in pressure. Under these conditions (termed Low Pressure Turbines) blading becomes strictly a reaction type design with the base of the blade solely impulse. The reason is due to the effect of the rotation speed for each blade. As the volume increases, the blade height increases, and the base of the blade spins at a slower speed relative to the tip. This change in speed forces a designer to change from impulse at the base, to a high reaction style tip.
Classical turbine design methods were developed in the mid 19th century. Vector analysis related the fluid flow with turbine shape and rotation. Graphical calculation methods were used at first. Formulas for the basic dimensions of turbine parts are well documented and a highly efficient machine can be reliably designed for any fluid flow condition. Some of the calculations are empirical or 'rule of thumb' formulae, and others are based on classical mechanics. As with most engineering calculations, simplifying assumptions were made.
Velocity triangles can be used to calculate the basic performance of a turbine stage. Gas exits the stationary turbine nozzle guide vanes at absolute velocity Va1. The rotor rotates at velocity U. Relative to the rotor, the velocity of the gas as it impinges on the rotor entrance is Vr1. The gas is turned by the rotor and exits, relative to the rotor, at velocity Vr2. However, in absolute terms the rotor exit velocity is Va2. The velocity triangles are constructed using these various velocity vectors. Velocity triangles can be constructed at any section through the blading (for example: hub , tip, midsection and so on) but are usually shown at the mean stage radius. Mean performance for the stage can be calculated from the velocity triangles, at this radius, using the Euler equation:
Whence:
where:
 acceleration of gravity
acceleration of gravity enthalpy drop across stage
enthalpy drop across stage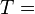 turbine entry total (or stagnation) temperature
turbine entry total (or stagnation) temperature turbine rotor peripheral velocity
turbine rotor peripheral velocity delta whirl velocity
delta whirl velocity
The turbine pressure ratio is a function of  and the turbine efficiency.
and the turbine efficiency.
Modern turbine design carries the calculations further. Computational fluid dynamics dispenses with many of the simplifying assumptions used to derive classical formulas and computer software facilitates optimization. These tools have led to steady improvements in turbine design over the last forty years.
The primary numerical classification of a turbine is its specific speed. This number describes the speed of the turbine at its maximum efficiency with respect to the power and flow rate. The specific speed is derived to be independent of turbine size. Given the fluid flow conditions and the desired shaft output speed, the specific speed can be calculated and an appropriate turbine design selected.
The specific speed, along with some fundamental formulas can be used to reliably scale an existing design of known performance to a new size with corresponding performance.
Off-design performance is normally displayed as a turbine map or characteristic.
[edit] Types of turbines
- Steam turbines are used for the generation of electricity in thermal power plants, such as plants using coal or fuel oil or nuclear power. They were once used to directly drive mechanical devices such as ship's propellors (eg the Turbinia), but most such applications now use reduction gears or an intermediate electrical step, where the turbine is used to generate electricity, which then powers an electric motor connected to the mechanical load.
- Gas turbine engines are sometimes referred to as turbine engines. Such engines usually feature an inlet, fan, compressor, combustor and nozzle (possibly other assemblies) in addition to one or more turbines.
- Transonic turbine. The gasflow in most turbines employed in gas turbine engines remains subsonic throughout the expansion process. In a transonic turbine the gasflow becomes supersonic as it exits the nozzle guide vanes, although the downstream velocities normally become subsonic. Transonic turbines operate at a higher pressure ratio than normal but are usually less efficient and uncommon. This turbine works well in creating power from water.
- Contra-rotating turbines. Some efficiency advantage can be obtained if a downstream turbine rotates in the opposite direction to an upstream unit. However, the complication may be counter-productive.
- Statorless turbine Multi-stage turbines have a set of static (meaning stationary) inlet guide vanes that direct the gasflow onto the rotating rotor blades. In a statorless turbine the gasflow exiting an upstream rotor impinges onto a downstream rotor without an intermediate set of stator vanes (that rearrange the pressure/velocity energy levels of the flow) being encountered.
- Ceramic turbine. Conventional high-pressure turbine blades (and vanes) are made from nickel-steel alloys and often utilise intricate internal air-cooling passages to prevent the metal from melting. In recent years, experimental ceramic blades have been manufactured and tested in gas turbines, with a view to increasing Rotor Inlet Temperatures and/or, possibly, eliminating aircooling. Ceramic blades are more brittle than their metallic counterparts, and carry a greater risk of catastrophic blade failure.
- Shrouded turbine. Many turbine rotor blades have a shroud at the top, which interlocks with that of adjacent blades, to increase damping and thereby reduce blade flutter.
- Shroudless turbine. Modern practise is, where possible, to eliminate the rotor shroud, thus reducing the centrifugal load on the blade and the cooling requirements.
- Bladeless turbine uses the boundary layer effect and not a fluid impinging upon the blades as in a conventional turbine.
- Water turbine
- Wind turbine. These normally operate as a single stage without nozzle and interstage guide vanes.
- Water and wind turbines have a thermodynamic cycle that is part of weather.
- Francis Turbine. Widely used water turbine.
- Kaplan Turbine. Variation of the Francis Turbine.
- Musser Turbine. A machine using four rotors to convert the static pressure of the working fluid into mechanical energy at a single output shaft. The intent of the design is to create a positive displacement turbine with relatively high flow handling characteristics.
[edit] Uses of turbines
Almost all electrical power on Earth is produced with a turbine of some type. Very high efficiency turbines harness about 40% of the thermal energy, with the rest exhausted as waste heat.
Most jet engines rely on turbines to supply mechanical work from their working fluid and fuel as do all nuclear ships and power plants.
Turbines are often part of a larger machine. A Gas turbine, for example, may refer to an internal combustion machine that contains a turbine, ducts, compressor, combustor, heat-exchanger, fan and (in the case of one designed to produce electricity) an alternator. However, it must be noted that the collective machine referred to as the turbine in these cases is designed to transfer energy from a fuel to the fluid passing through such an internal combustion device as a means of propulsion, and not to transfer energy from the fluid passing through the turbine to the turbine as is the case in turbines used for electricity provision etc.
Reciprocating piston engines such as aircraft engines can use a turbine powered by their exhaust to drive an intake-air compressor, a configuration known as a turbocharger (turbine supercharger) or, colloquially, a "turbo".
Turbines can have incredible power density (with respect to volume and weight). This is because of their ability to operate at very high speeds. The Space Shuttle's main engines use turbopumps (machines consisting of a pump driven by a turbine engine) to feed the propellants (liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen) into the engine's combustion chamber. The liquid hydrogen turbopump is slightly larger than an automobile engine (weighing approximately 700 lb) and produces nearly 70,000 hp (52.2 MW).
Turboexpanders are widely used as sources of refrigeration in industrial processes.
[edit] Shrouded Tidal turbines
An emerging renewable energy technology is the shrouded tidal turbine enclosed in a Venturi shaped shroud or duct producing a sub atmosphere of low pressure behind the turbine, allowing the turbine to operate at higher efficiency (than the Betz Limit [1] of 59.3%) and typically 3 times higher power output [2] than a turbine of the same size in free stream.
As shown in the CFD (Computational Fluid Dynamics) generated figure here it can be seen that a down stream low pressure (shown by the gradient lines) draws upstream flow into the inlet of the shroud from well outside the inlet of the shroud. This flow is drawn into the shroud and concentrated (as seen by the red coloured zone). This augmentation of flow velocity corresponds to a 3-4 times increase in energy available to the turbine. Therefore a turbine located in the throat of the shroud is then able to achieve higher efficiency, and an output 3-4 times the energy the turbine would be capable of if it were in open or free stream. For this reason shrouded turbines are not subject to the properties of the Betz Limit.
Considerable commercial interest has been shown in recent times in shrouded tidal turbines as it allows a smaller turbine to be used at sites where large turbines are restricted. Arrayed across a seaway or in fast flowing rivers shrouded tidal turbines are easily cabled to a terrestrial base and connected to a grid or remote community. Alternatively the property of the shroud that produces an accelerated flow velocity across the turbine allows tidal flows formerly too slow for commercial use to be utilised for commercial energy production.
While the shroud may not be practical in wind, as a tidal turbine it is gaining more popularity and commercial use. A shrouded tidal turbine is mono directional and constantly needs to face upstream in order to operate. It can be floated under a pontoon on a swing mooring, fixed to the seabed on a mono pile and yawed like a wind sock to continually face upstream. A shroud can also be built into a tidal fence increasing the performance of the turbines.
Cabled to the mainland they can be grid connected or can be scaled down to provide energy to remote communities where large civil infrastructures are not viable. Similarly to tidal stream open turbines they have little if any environmental or visual amenity impact.
BW Bewise Inc. Willy Chen willy@tool-tool.com bw@tool-tool.com www.tool-tool.com skype:willy_chen_bw mobile:0937-618-190 Head &Administration Office No.13,Shiang Shang 2nd St., West Chiu Taichung,Taiwan 40356 TEL:+886 4 24710048 / FAX:+886 4 2471 4839 N.Branch 5F,No.460,Fu Shin North Rd.,Taipei,Taiwan S.Branch No.24,Sec.1,Chia Pu East Rd.,Taipao City,Chiayi Hsien,Taiwan
Welcome to BW tool world! We are an experienced tool maker specialized in cutting tools. We focus on what you need and endeavor to research the best cutter to satisfy users’ demand. Our customers involve wide range of industries, like mold & die, aerospace, electronic, machinery, etc. We are professional expert in cutting field. We would like to solve every problem from you. Please feel free to contact us, its our pleasure to serve for you. BW product including: cutting tool、aerospace tool .HSS Cutting tool、Carbide end mills、Carbide cutting tool、NAS Cutting tool、Carbide end mill、Aerospace cutting tool、Фрезеры’Carbide drill、High speed steel、Milling cutter、CVDD(Chemical Vapor Deposition Diamond )’PCBN (Polycrystalline Cubic Boron Nitride) ’Core drill、Tapered end mills、CVD Diamond Tools Inserts’PCD Edge-Beveling Cutter(Golden Finger’PCD V-Cutter’PCD Wood tools’PCD Cutting tools’PCD Circular Saw Blade’PVDD End Mills’diamond tool ‘Single Crystal Diamond ‘Metric end mills、Miniature end mills、Специальные режущие инструменты ‘Пустотелое сверло ‘Pilot reamer、Fraises’Fresas con mango’ PCD (Polycrystalline diamond) ‘Frese’Electronics cutter、Step drill、Metal cutting saw、Double margin drill、Gun barrel、Angle milling cutter、Carbide burrs、Carbide tipped cutter、Chamfering tool、IC card engraving cutter、Side cutter、NAS tool、DIN tool、Special tool、Metal slitting saws、Shell end mills、Side and face milling cutters、Side chip clearance saws、Long end mills、Stub roughing end mills、Dovetail milling cutters、Carbide slot drills、Carbide torus cutters、Angel carbide end mills、Carbide torus cutters、Carbide ball-nosed slot drills、Mould cutter、Tool manufacturer.
Bewise Inc. www.tool-tool.com
BW специализируется в научных исследованиях и разработках, и снабжаем самым высокотехнологичным карбидовым материалом для поставки режущих / фрезеровочных инструментов для почвы, воздушного пространства и электронной индустрии. В нашу основную продукцию входит твердый карбид / быстрорежущая сталь, а также двигатели, микроэлектрические дрели, IC картонорезальные машины, фрезы для гравирования, режущие пилы, фрезеры-расширители, фрезеры-расширители с резцом, дрели, резаки форм для шлицевого вала / звездочки роликовой цепи, и специальные нано инструменты. Пожалуйста, посетите сайт www.tool-tool.com для получения большей информации.
BW is specialized in R&D and sourcing the most advanced carbide material with high-tech coating to supply cutting / milling tool for mould & die, aero space and electronic industry. Our main products include solid carbide / HSS end mills, micro electronic drill, IC card cutter, engraving cutter, shell end mills, cutting saw, reamer, thread reamer, leading drill, involute gear cutter for spur wheel, rack and worm milling cutter, thread milling cutter, form cutters for spline shaft/roller chain sprocket, and special tool, with nano grade. Please visit our web www.tool-tool.com for more info.










